
- #GMSH EMBED VOLUME HOW TO#
- #GMSH EMBED VOLUME SOFTWARE#
There are different possibilities to set up a mesh in the FEM Workbench: A balance between the size of the mesh, and computation time and accuracy of results is an important characteristic of a well defined finite element analysis. The more refined the mesh is, the more accurate the numerical results will be, but also the computation time will be larger.
 6.14 Volume, 13 node pyramid, pyra13 (quadratic)įinite element analysis (FEA) is performed on a mesh composed of multiple triangular and quadrilateral finite elements that subdivide an original body. 6.13 Volume, 5 node pyramid, pyra5 (linear). 6.12 Volume, 15 node pentahedron, penta15 (quadratic). 6.11 Volume, 6 node pentahedron, penta6 (linear). 6.10 Volume, 20 node hexahedron, hexa20 (quadratic). 6.9 Volume, 8 node hexahedron, hexa8 (linear). 6.8 Volume, 10 node tetrahedron, tetra10 (quadratic). 6.7 Volume, 4 node tetrahedron, tetra4 (linear). 6.6 Shell, 8 node quadrangle, quad8 (quadratic). 6.5 Shell, 4 node quadrangle, quad4 (linear). 6.4 Shell, 6 node triangle, tria6 (quadratic). 6.3 Shell, 3 node triangle, tria3 (linear). 6.2 Beam, 3 node line, seg3 (quadratic). 6 Scripting examples of each supported element type. 5.1.1 Creating a mesh with one Tet-10 element. 5.1 Create a FEM mesh completely in Python. Thanks to Loïc Norgeot, you can use BakeMyScan, an Open Source toolbox for asset optimization, to call mmgs inside Blender. YALES2: a solver for two-phase combustion, from primary atomization to pollutant prediction, on massive complex meshes. MUSIC: a multimodal platform for cardiac imagery.
6.14 Volume, 13 node pyramid, pyra13 (quadratic)įinite element analysis (FEA) is performed on a mesh composed of multiple triangular and quadrilateral finite elements that subdivide an original body. 6.13 Volume, 5 node pyramid, pyra5 (linear). 6.12 Volume, 15 node pentahedron, penta15 (quadratic). 6.11 Volume, 6 node pentahedron, penta6 (linear). 6.10 Volume, 20 node hexahedron, hexa20 (quadratic). 6.9 Volume, 8 node hexahedron, hexa8 (linear). 6.8 Volume, 10 node tetrahedron, tetra10 (quadratic). 6.7 Volume, 4 node tetrahedron, tetra4 (linear). 6.6 Shell, 8 node quadrangle, quad8 (quadratic). 6.5 Shell, 4 node quadrangle, quad4 (linear). 6.4 Shell, 6 node triangle, tria6 (quadratic). 6.3 Shell, 3 node triangle, tria3 (linear). 6.2 Beam, 3 node line, seg3 (quadratic). 6 Scripting examples of each supported element type. 5.1.1 Creating a mesh with one Tet-10 element. 5.1 Create a FEM mesh completely in Python. Thanks to Loïc Norgeot, you can use BakeMyScan, an Open Source toolbox for asset optimization, to call mmgs inside Blender. YALES2: a solver for two-phase combustion, from primary atomization to pollutant prediction, on massive complex meshes. MUSIC: a multimodal platform for cardiac imagery. #GMSH EMBED VOLUME SOFTWARE#
Kratos: a framework for building parallel, multi-disciplinary simulation software (open source).Gypsilab: a MATLAB toolbox for fast numerical computation with finite element and boundary element methods (open source).Freefem++:a partial differential equation solver for non-linear multi-physics systems in 2D and 3D (open source).Elmer/Ice: a finite element software for ice sheet, glaciers and ice flow modelling (open source).AVBP : a solver for numerical simulation of unsteady turbulence for reacting flows.If you don’t have a favorite solver yet, you can use one of those that interfaces Mmg: Of course the meshes generated by Mmg can be used in any solver. paraview: allows to visualize your mesh and solution at the VTK file formats.medit: allows to visualize your mesh and solution at the medit format.gmsh: allows to visualize your mesh at the medit format (but not the associated solution) and, of course, your mesh at the gmsh format and its embedded solution.
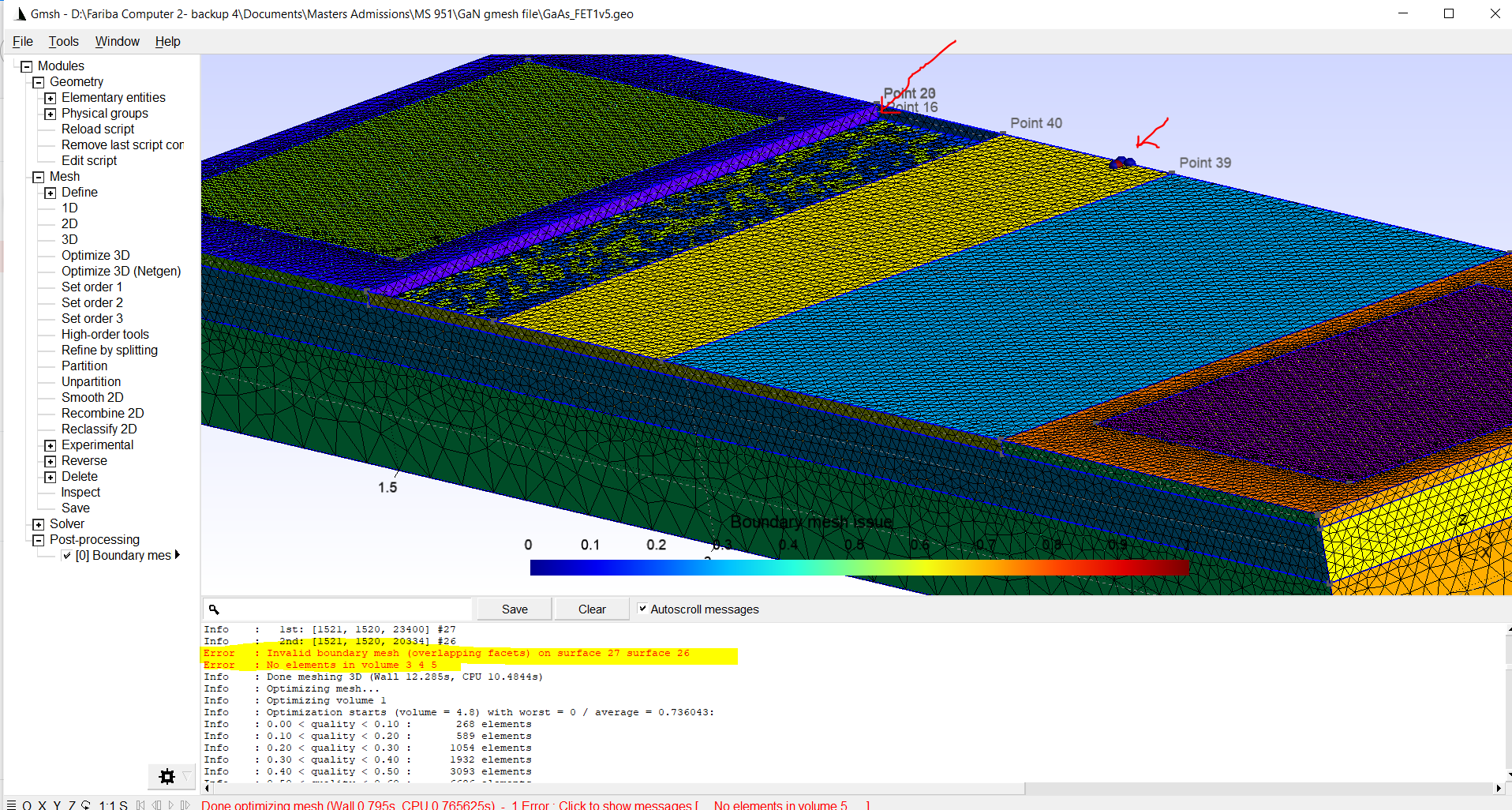
#GMSH EMBED VOLUME HOW TO#
How to prescribe an anisotropic size map? Mesh visualization: Practical work to learn how to use Mmg (applications and libraries): To learn how to use the Mmg libraries: go here Lot of options are commons between the four codes, thus, do not hesitate to look at the tutorials of the four software to understand how to use it.
mmg3d tutorials to learn how to remesh tetrahedral volume meshes. mmgs tutorials to learn how to remesh triangular three-dimensional surface meshes. mmg2d tutorialsto learn how to remesh triangular two-dimensional meshes. Remark: you must provide positive or null integers for the entities references. point data) with the medit:ref array name. node references) can be provided using cell data (resp. the level-set or displacement must be provided in the mesh file as point data. the size map must be provided in the mesh file as point data and named with the :metric suffix. mesh file, you can run mmg2d with the – 3dMedit 3 command line argument. mesh file created with Gmsh and to save it as a Medit 2D. mesh file created with Gmsh, you will need to run mmg2d with the -3dMedit 2 command line argument. mesh file readable by Gmsh (not anymore compatible with Medit) you can run mmg2d with the -3dMedit 1 command line argument. mesh format used by mmg2d (coordinates in 2D) and the gmsh output (coordinates in 3D): there is a non-compatibility between the. the level-set or displacement must be provided in the. msh(b) file as $NodeData and flagged using a string tag with the :metric suffix. a displacement at medit solution file format (.sol extension) if you want to perform the lagrangian motion of an object. a level-set at medit solution file format (.sol extension) if you want to discretize an isovalue of a function. a size map at medit solution file format (.sol extension) if you want to adapt your mesh to a size map. If you use the medit file format, you can provide: Note that the gmsh software handles a lot of mesh file formats, thus, you can use it to convert your mesh at the medit format : Save As -> Mesh - INRIA Medit (*.mesh) if you have access to the VTK library built with MPI support ( VTK_USE_MPI CMake’s flag setted to ON). a conformal mesh at the medit file format (.mesh(b) extension) or at the gmsh file format (.msh(b) extension).






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
